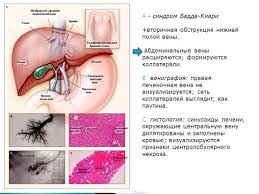
Budd-Chiari disease - primary veno-occlusive disease of the liver with thrombosisand subsequent occlusion, anddevelopmental anomalies of the hepatic veins, leading to violations of the outflow of blood from the liver.
Budd-Chiari syndrome - secondary infringement of outflow of blood from the liverin several pathological conditions notassociated with changes in blood vessels of the liver.
Causes
Congenital anomalies of the hepatic vessels
injuries
Violations of the blood coagulation system
pregnancy
childbirth
Surgeries
vasculitis
Prolonged intake of hormonal contraceptives
Observed in peritonitis, abdominal tumors, pericarditis, thrombosis and malformations of the inferior venacava, cirrhosis and focal liver lesions, visceral migrating thrombophlebitis, polycythemia.
By the nature of the disease was isolated acute, subacute and chronic forms.
The acute form of the disease begins abruptly with the appearance of intense pain in the epigastric and right upper quadrant, vomiting, liver enlargement. With involvement of the inferior vena cava observed lower limb edema, expansion of the subcutaneous veins of the anterior abdominal wall of the chest. The diseaseprogresses rapidly, within a few days of developing ascites, often having hemorrhagic in nature. Sometimesascites can be combined with hydrothorax not treatable with diuretics.
In the chronic form (80-85%) endoflebit long asymptomatic or manifest only hepatomegaly. Subsequentlyobserved in the right upper quadrant pain, and vomiting. In the advanced stage of liver markedly increases in size, becomes dense, possibly formation of liver cirrhosis in some cases appear splenomegaly, dilated veins on the anterior abdominal wall and chest. In end-stage revealed pronounced signs of portal hypertension. In some cases, the syndrome of the inferior vena cava. Outcome of the disease is severe liver failure, thrombosis ofmesenteric vessels. Jaundice is rare. The appearance of peripheral edema suggesting thrombosis orcompression of the inferior vena cava. If such patients are not given the necessary medical care, they die due to complications of portal hypertension.
Conservative therapy provides only temporary symptomatic effect. Mortality using conservative therapy is 85-90%.
Forecast:
The acute form usually leads to hepatic coma and death of the patient. Life expectancy of patients with long-term process during limited symptomatic treatment up to several years. Forecast is largely determined etiologysyndrome prevalence occlusion and possibly fix it.

