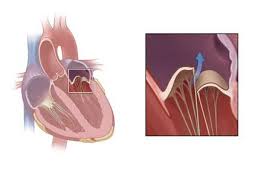
Mitral regurgitation (MR), mitral insufficiency or >mitral incompetence is a disorder of the heart in which the mitral valve does not close properly when the heart pumps out blood. It is the abnormal leaking of blood from the left ventricle, through the mitral valve, and into the left atrium, when the left ventricle contracts, i.e. there is regurgitation of blood back into the left atrium. MR is the most common form of valvular heart disease.
Symptoms and signs
The symptoms associated with mitral regurgitation are dependent on which phase of the disease process the individual is in. Individuals with acute mitral regurgitation will have the signs and symptoms of decompensated congestive heart failure(i.e. shortness of breath, pulmonary edema, orthopnea, and paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea), as well as symptoms suggestive of a low cardiac output state (i.e. decreased exercise tolerance). Palpitations are also common. Cardiovascular collapse with shock (cardiogenic shock) may be seen in individuals with acute mitral regurgitation due to papillary muscle rupture or rupture of a chorda tendinea.
Individuals with chronic compensated mitral regurgitation may be asymptomatic, with a normal exercise tolerance and no evidence of heart failure. These individuals may be sensitive to small shifts in their intravascular volume status, and are prone to develop volume overload (congestive heart failure).
Findings on clinical examination depend on the severity and duration of mitral regurgitation. The mitral component of the first heart sound is usually soft and with a laterally displaced apex beat, often with heave. The first heart sound is followed by a high-pitched holosystolic murmur at the apex, radiating to the back or clavicular area. Its duration is, as the name suggests, the whole of systole. The loudness of the murmur does not correlate well with the severity of regurgitation. It may be followed by a loud, palpable P2, heard best when lying on the left side. A third heart sound is commonly heard.
Commonly, atrial fibrillation is found.
In acute cases, the murmur and tachycardia may be only distinctive signs.
Patients with mitral valve prolapse often have a mid-to-late systolic click and a late systolic murmur.

