In medicine, Raynaud's phenomenon or Raynaud phenomenon is excessively reduced blood flow in response to cold or emotional stress, causing discoloration of the fingers, toes, and occasionally other areas. This condition may also cause nails to become brittle with longitudinal ridges. Named after French physician Maurice Raynaud (1834–1881), the phenomenon is believed to be the result of vasospasms that decrease blood supply to the respective regions.
Raynaud's phenomenon by itself is just a sign (hypoperfusion) accompanied by a symptom (discomfort). When linked to pathogenesis, it can be part of Raynaud's disease (also known as primary Raynaud's phenomenon), where the cause is unknown, or part of Raynaud's syndrome (secondary Raynaud's phenomenon), which is a syndrome caused by a known primary disease, most commonly connective tissue disorders such as systemic lupus erythematosus. Measurement of hand-temperature gradients is one tool used to distinguish between the primary and secondary forms.
It is a hyperactivation of the sympathetic nervous system causing extreme vasoconstriction of the peripheral blood vessels, leading to tissue hypoxia. Chronic, recurrent cases of Raynaud phenomenon can result in atrophy of the skin,subcutaneous tissues, and muscle. In rare cases it can cause ulceration and ischemic gangrene.
Symptoms
The condition can cause pain within the affected extremities, discoloration (paleness), and sensations of cold and/or numbness. This can often be distressing to those who are not diagnosed, and sometimes it can be obstructive. If someone with Raynaud's is placed in too cold a climate, it could potentially become dangerous.
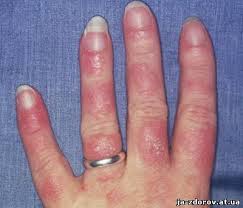
- All three color changes are observed in classic Raynaud's. However, not all patients see all of the aforementioned color changes in all episodes, especially in milder cases of the condition. Symptoms are thought to be due to reactive hyperemias of the areas deprived of blood flow.When exposed to cold temperatures, the blood supply to the fingers or toes, and in some cases the nose or earlobes, is markedly reduced; the skin turns pale or white (called pallor), and becomes cold and numb.
- When the oxygen supply is depleted, the skin color turns blue (called cyanosis).
- These events are episodic, and when the episode subsides or the area is warmed, the blood flow returns and the skin color first turns red (rubor), and then back to normal, often accompanied by swelling, tingling, and a painful "pins and needles" sensation.
In pregnancy, this sign normally disappears owing to increased surface blood flow. Raynaud's also has occurred in breastfeeding mothers, causing nipples to turn white and become extremely painful. Nifedipine, a calcium channel blocker andvasodilator, was recommended to increase blood flow to the extremities and noticeably relieved pain to the breast in an extremely small study group.

